
Ekimmu Vampires
The first myth on Vampires predates back to roughly 4000 B.C.E. from the ancient Sumer civilization. The ancient Sumerians existed in Mesopotamia and facts prove that by 3100 B.C.E., their culture brought the earliest archeologically proven dynasty; the first cities were built along with establishing the city and state religions were set up and practiced. The Sumerians is the first civilization to receive our attention as the first and oldest myth of a Vampire-like being that is the Ekimmu.
The Ekimmu, like many Vampires of folklore, was believed to have been created when someone died a violent death or was not buried properly. Although not referred to out right as a Vampire, the way they are described as helps us to draw the conclusion that these creatures were real intentional psychic Vampires. They were described as demonic in nature, severely rotting corpses, phantom-like entities that roamed the earth, unable to rest, in search of victims. In reference to The Devils and Evil Spirits of Babylonia, by R. Campbell Thompson, the creatures preferred the attack pattern of finding a helpless individual, then tormenting this victim until a priest or priestess could come and perform a ritual or exorcism to force the Vampire off.
Uruku a.k.a. Utukku
Another creature from the Mesopotamian that fits this role as Vampire-like creatures is that of the Uruku or Utukku. The Uruku is actually referred to as a “Vampyre which attacks man” in a cuneiform inscription. There is very little known about the Uruku, but, the mere fact that it has been referred to as a “Vampire” deems it worthy to mention here.
The Seven Demons
Another “race” of Vampires is also mentioned as a Vampiric entity which was much feared: “The Seven Demons.” These beings have been mentioned in many Mesopotamian religious texts and incantations, like the following excerpt taken from a Sumerian banishment (taken from The Devils and Evil Spirits of Babylonia, by R. Campbell Thompson):
Demons that have no shame,
Seven are they!
Knowing no care.
Knowing no mercy,
They rage against mankind:
Devouring their flesh and sucking their veins.
Where the images of the gods are they quake.
They are demons full of violence
Ceaselessly devouring blood.
Invoke the ban against them,
That they no more return to this neighborhood.
The creatures described above clearly have attributes similar to immortal blood-drinking Vampires. The blood drinking and vein sucking make it clear to assume that they are Vampires of some sort indeed. The eighth line in the excerpt indicates that the creatures are afraid of the images of the Sumer gods, or of the temples in which most god images are kept.

Measures of Time:
CE stands for “Common Era.” AD is an abbreviation for “Anno Domini” in Latin or “the year of the Lord” in English. Both measure the number of years since the approximate birthday of Yeshua of Nazareth (a.k.a. Jesus Christ) a little over two millennia ago. CE and AD have the same value. That is 1 CE = 1 AD, and 2011 CE = 2011 AD. The word “common” simply means that it is based on the most frequently used calendar system: the Gregorian Calendar.
BCE stands for “Before the common era.” BC means “Before Christ,” or “Before the Messiah.” Both measure the number of years before the approximate birthday of Yeshua/Jesus. A year in BC and BCE also have identical values.
Although many people believe that Yeshua/Jesus was born at the end of 1 BCE, most theologians and religious historians estimate that he was born in the fall of a year, sometime between 7 and 4 BCE. However, we have seen estimates as late as 4 CE and as early as the second century BCE.
Of course, one has the option of interpreting the letter “C” in CE and BCE as referring to “Christian” or “Christ’s” The Abbreviations Dictionary does exactly this. The “C” has also been interpreted as “Current.”
Vampire skeletons unearthed in Bulgaria
Skeletons treated for vampirism found in Bulgaria
Associated Press

Archaeologists in Bulgaria have unearthed two skeletons from the Middle Ages pierced through the chest with iron rods to keep them from turning into vampires, the head of the national history museum says.
According to pagan beliefs, people who were considered bad during their lifetimes might turn into vampires after death unless stabbed in the chest with an iron or wooden rod before being buried.
‘These two skeletons stabbed with rods illustrate a practice which was common in some Bulgarian villages up until the first decade of the 20th century,’ national history museum chief Bozhidar Dimitrov said after the recent find in the Black Sea town of Sozopol.
People believed the rod would also pin the dead into their graves to prevent them from leaving at midnight and terrorizing the living, the historian explained.
The practice was common, Dimitrov added, saying some 100 similar burials had already been found in Bulgaria.
Archaeologist Petar Balabanov, who in 2004 unearthed six nailed-down skeletons at a site near the eastern town of Debelt, said the pagan rite was also practiced in neighboring Serbia and other Balkan countries.
Vampire legends are widespread across the Balkans. The most famous is that of Romanian count Vlad the Impaler, known as Dracula, who staked his war enemies and drank their blood.
Now, for the deep dive, enjoy. 🙂
Are you sure digging him up is a good idea? Archaeologists find Bulgarian ‘vampires’ from Middle Ages with iron rods staked through their chests
If you thought vampires were simply the stuff of myth and legend – and perhaps the odd teen horror film – think again.
Archaeologists in Bulgaria have unearthed two skeletons from the Middle Ages pierced through the chest with iron rods to keep them from turning into the undead.
They are the latest in a succession of finds across western and central Europe which shed new light on just how seriously people took the threat of vampires and how those beliefs transformed into the modern myth.
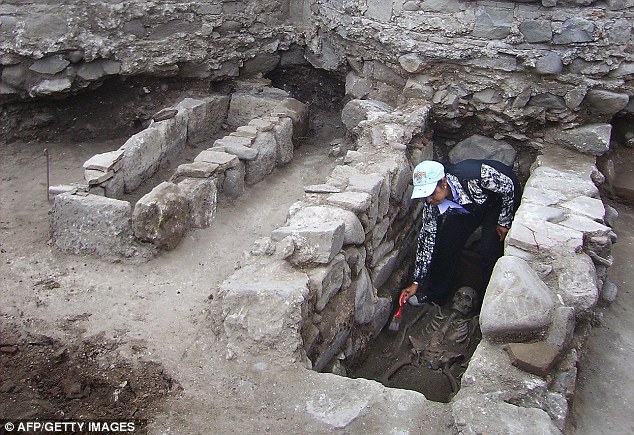

The two skeletons, believed to be around 800 years old, were discovered during an archaeological dig near a monastery in the Bulgarian Black Sea town of Sozopol.
Bulgaria’s national history museum chief Bozhidar Dimitrov said: ‘These two skeletons stabbed with rods illustrate a practice which was common in some Bulgarian villages up until the first decade of the 20th century.’

According to pagan beliefs, people who were considered bad during their lifetimes might turn into vampires after death unless stabbed in the chest with an iron or wooden rod before being buried.
People believed the rod would also pin them down in their graves to prevent them from leaving at midnight and terrorizing the living, the historian explained.
According to Mr Dimitrov over 100 buried people whose corpses were stabbed to prevent them from becoming vampires have been discovered across Bulgaria over the years.
He added: ‘I do not know why an ordinary discovery like that became so popular. Perhaps because of the mysteriousness of the word “vampire.”
‘These people were believed to be evil while they were alive, and it was believed that they would become vampires once they are dead, continuing to torment people.’
According to Dimitrov, ‘vampires’ were often aristocrats and clerics.
He added: ‘The curious thing is that there are no women among them. They were not afraid of witches.’
However last month Italian researchers discovered what they believed to be the remains of a female ‘vampire’ in Venice – buried with a brick jammed between her jaws to prevent her feeding on victims of a plague which swept the city in the 16th century.
Matteo Borrini, an anthropologist from the University of Florence, said the discovery on the small island of Lazzaretto Nuovo in the Venice lagoon supported the medieval belief that vampires were behind the spread of plagues like the Black Death.
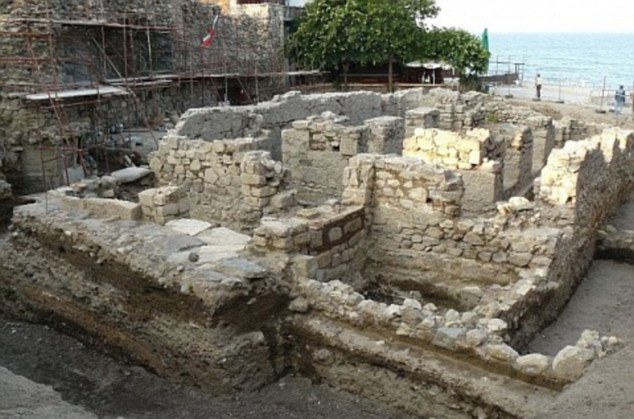
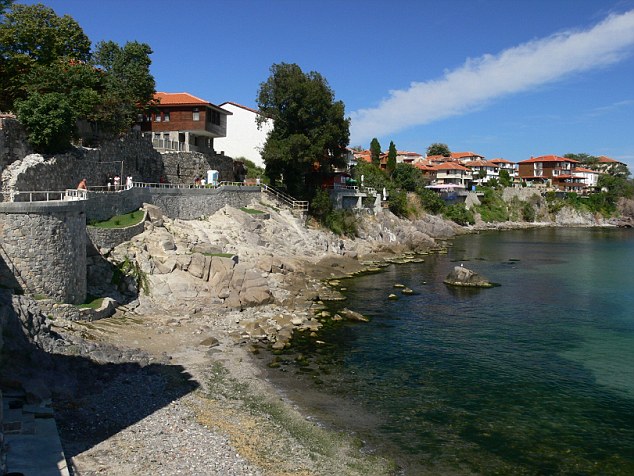


The skeleton was unearthed in a mass grave from the Venetian plague of 1576 – in which the artist Titian died – on Lazzaretto Nuovo, which lies around two miles northeast of Venice and was used as a sanitarium for plague sufferers.
Borrini said: ‘This is the first time that archaeology has succeeded in reconstructing the ritual of exorcism of a vampire.
‘This helps authenticate how the myth of vampires was born.’
The succession of plagues which ravaged Europe between 1300 and 1700 fostered the belief in vampires, mainly because the decomposition of corpses was not well understood, Borrini said.
Gravediggers reopening mass graves would sometimes come across bodies bloated by gas, with hair still growing, and blood seeping from their mouths and believe them to be still alive.
The shrouds used to cover the faces of the dead were often decayed by bacteria in the mouth, revealing the corpse’s teeth, and vampires became known as ‘shroud-eaters.’
According to medieval medical and religious texts, the ‘undead’ were believed to spread pestilence in order to suck the remaining life from corpses until they acquired the strength to return to the streets again.
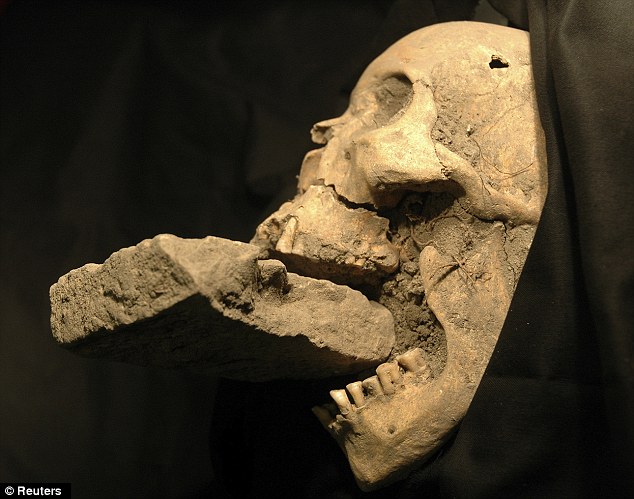
‘To kill the vampire you had to remove the shroud from its mouth, which was its food like the milk of a child, and put something uneatable in there,’ said Borrini.
‘It’s possible that other corpses have been found with bricks in their mouths, but this is the first time the ritual has been recognized.’
While legends about blood-drinking ghouls date back thousands of years, the modern figure of the vampire was encapsulated in the Irish author Bram Stoker’s 1897 novel ‘Dracula,’ based on 18th century eastern European folktales.
BATTY BELIEFS: EUROPE’S FEAR OF VAMPIRES IN THE MIDDLE AGES
The belief in vampires was widespread throughout Bulgaria and other parts of central Europe throughout the Middle Ages.
The word vampire is derived from the original Slavic term opyrb or opir which later appears as vipir, vepir, or vapir.
Drunkards, thieves and murderers were all believed to be likely candidates to become vampires.

Appearing completely normal, they would arrive at a town and live amongst the people often even marrying and fathering children. But at night they would wander the countryside in search of blood.
These types of vampires could be destroyed with a stake through the heart.
One account maintains that a vampire was the soul of an outlaw who died in the mountains or forest or along a country road, and whose corpse is eaten by crows, wolves, or some other such scavengers.
Because such a soul is not permitted to enter heaven or hell it remains on earth haunting the place where he was killed strangling and drinking the blood of anyone who comes by.
Another account states a person who died a violent, unnatural death or whose corpse was jumped over by a cat before burial, can become a vampire.
In such cases during the first 40 days after burial, the bones turn to gelatin and the vampire performs mischief at night – releasing animals from their pens, scattering house hold items, and suffocating people.
During the first forty days it can be destroyed by a Vampiridzhija – a professional vampire hunter capable of seeing them – or alternatively devoured by a wolf.
However if not destroyed in this time period the Vampire would develop a skeleton and becomes even more fierce.
In other areas, the unexplained deaths of cattle or other livestock were often taken as proof that a type of vampire known as an Ustrel was at large.
These were believed to be the spirits of children born on a Saturday but who died before receiving baptism.
On the ninth day after its burial, a Ustrel would climb out of the ground and attack cattle or sheep by draining their blood before returning to its grave before dawn.
To kill an Ustrel, a village would have to go through a ritual known as lighting of a needfire.
This involved extinguishing all the village household fires on a Saturday morning before rounding up all the cattle and sheep in an open space.
From there the animals were marched to a nearby crossroads where two bonfires, lit by a new fire created by rubbing sticks together, had been set up.
By guiding the animals between the fires the vampire would become stranded at the crossroads where wolves devoured it.
Before the bonfires burned out, someone took a flame and used it to relight all the household fires in the village.